Understanding diabetes and its impact on sugar consumption
Living with diabetes requires careful management of one’s diet, with particular attention to the intake of sugar. For individuals with diabetes, consuming excessive amounts of sugar can lead to spikes in blood glucose levels, increasing the risk of complications. Therefore, finding suitable sugar substitutes becomes essential in maintaining a balanced and healthy lifestyle. In this article, we will explore the world of sugar substitutes and provide valuable insights into incorporating them into a diabetic diet.
The need for sugar substitutes in a diabetic diet
Diabetes, a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels, poses numerous challenges for those affected. Managing blood glucose levels is crucial for preventing long-term complications. With the prevalence of sugar in many foods, it presents a dilemma for individuals with diabetes who need to satisfy their sweet tooth while maintaining stable blood sugar levels. This is where sugar substitutes come into play.
Different types of sugar substitutes
Sugar substitutes are alternatives to traditional sugar that provide a sweet taste without the negative effects on blood glucose levels. They can be broadly classified into two categories: natural sugar substitutes and artificial sugar substitutes.
Natural sugar substitutes for diabetics

Natural sugar substitutes are derived from plant sources and offer a healthier alternative to refined sugar. Stevia, extracted from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant, is one such example. It is a non-caloric sweetener that does not impact blood glucose levels. Another natural option is monk fruit extract, which provides sweetness without the added calories or carbohydrates.
Artificial sugar substitutes for diabetics
Artificial sugar substitutes, also known as non-nutritive sweeteners, are synthetically produced and provide sweetness without the calories or carbohydrates found in sugar. Common examples include aspartame, sucralose, and saccharin. These sugar substitutes are significantly sweeter than sugar, allowing for smaller quantities to achieve the desired level of sweetness.
How to incorporate sugar substitutes into your diet
Incorporating sugar substitutes into a diabetic diet requires a thoughtful approach. Here are some practical tips to help you navigate the world of sugar substitutes:
- Gradual transition: Start by gradually reducing your sugar intake and replacing it with sugar substitutes. This will allow your taste buds to adjust to the new flavors.
- Experiment with different substitutes: Try various natural and artificial sugar substitutes to find the ones that suit your taste preferences. Everyone’s palate is different, so don’t be discouraged if the first substitute you try doesn’t meet your expectations.
- Read labels: When purchasing packaged foods, carefully read the labels to identify hidden sugars. Some products may claim to be sugar-free but contain other sweeteners that can still affect blood glucose levels.
Read : 5 Sugar Free Juices Especially for Diabetics to Quench Summer Thirst !
Pros and cons of sugar substitutes for diabetics
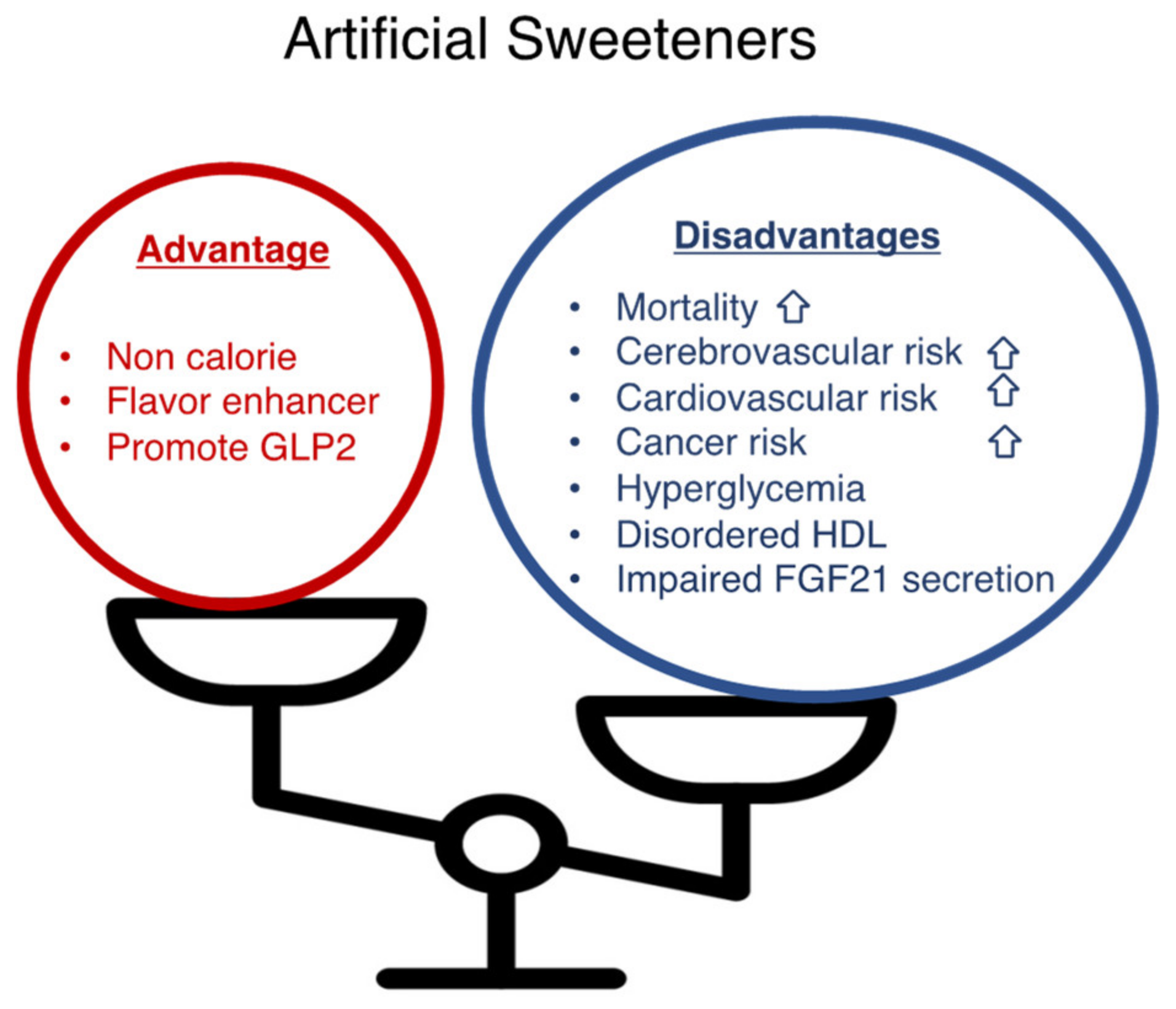
Like any dietary choice, sugar substitutes have their advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions about incorporating them into your diet.
Pros of sugar substitutes for diabetics
- Blood glucose control: Sugar substitutes do not cause a rapid increase in blood glucose levels, making them a suitable alternative for individuals with diabetes.
- Weight management: Sugar substitutes are often lower in calories than sugar, making them a valuable tool for those looking to manage or lose weight.
Cons of sugar substitutes for diabetics
- Taste differences: Sugar substitutes may have a slightly different taste compared to sugar, which can take some getting used to.
- Potential digestive effects: Some individuals may experience digestive issues, such as bloating or diarrhea, when consuming certain sugar substitutes. It is important to listen to your body and make adjustments accordingly.
Sugar substitute myths and misconceptions
There are several myths and misconceptions surrounding sugar substitutes that can lead to confusion. Let’s debunk some of the most common ones:
- Sugar substitutes are completely safe: While sugar substitutes are generally considered safe, it is important to consume them in moderation. Some studies suggest that excessive consumption of certain sugar substitutes may have negative health effects.
- Sugar substitutes are the solution to weight loss: While sugar substitutes can be helpful in managing calorie intake, they should not be seen as a magic solution for weight loss. A balanced diet and regular exercise remain key components of a healthy lifestyle.
Reading labels: Identifying hidden sugars in products
When it comes to managing sugar intake, reading product labels becomes crucial. Many foods, even those marketed as “healthy,” can contain hidden sugars that can negatively impact blood glucose levels. Here are some tips for deciphering food labels:
- Look for hidden sugar names: Sugar can hide under various names, such as high-fructose corn syrup, maltose, dextrose, or fruit juice concentrate. Familiarize yourself with these names to identify added sugars in products.
- Check the ingredient list: Ingredients are listed in descending order of quantity. If sugar or its various names appear high up on the list, it indicates a higher sugar content.
Sugar substitute recommendations for diabetics
Here are some popular sugar substitutes that are suitable for individuals with diabetes:
- Stevia: A natural, non-caloric sweetener derived from the leaves of the Stevia rebaudiana plant.
- Monk fruit extract: A natural sweetener with zero calories and carbohydrates, derived from the monk fruit.
- Erythritol: A sugar alcohol that provides sweetness without raising blood sugar levels.
- Sucralose: An artificial sweetener that is heat-stable and can be used in cooking and baking.
Remember, finding the right sugar substitute is a personal journey, and it may take some experimentation to discover your preferred options.
In conclusion, sugar substitutes offer a valuable solution for individuals with diabetes who want to enjoy sweetness without compromising their health. By understanding the different types of sugar substitutes, incorporating them into your diet, and reading labels diligently, you can navigate the sweet world of healthier options and maintain a balanced diabetic lifestyle.
Conclusion: Finding the right sugar substitute for your diabetic lifestyle
Navigating the sweet world of sugar substitutes can be overwhelming, but with the right knowledge, it becomes easier to make informed choices. Consider your taste preferences, health goals, and any potential digestive issues when selecting sugar substitutes. Remember to consult with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
Note: Speak with your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian to learn more about sugar substitutes and their suitability for your specific dietary needs.

