But don’t panic just yet! While pregnancy complications are a reality for some, knowledge is power. Understanding the common problems, recognizing risk factors, and learning prevention strategies can significantly improve your chances of a healthy pregnancy. Whether you’re a first-time mom or a seasoned parent, staying informed is crucial for both you and your baby’s well-being.
In this blog post, we’ll delve into the world of pregnancy complications, exploring the most common issues, identifying key risk factors, and providing practical tips for prevention. By the end, you’ll be equipped with the information you need to navigate your pregnancy journey with confidence and peace of mind. Let’s embark on this important exploration together!
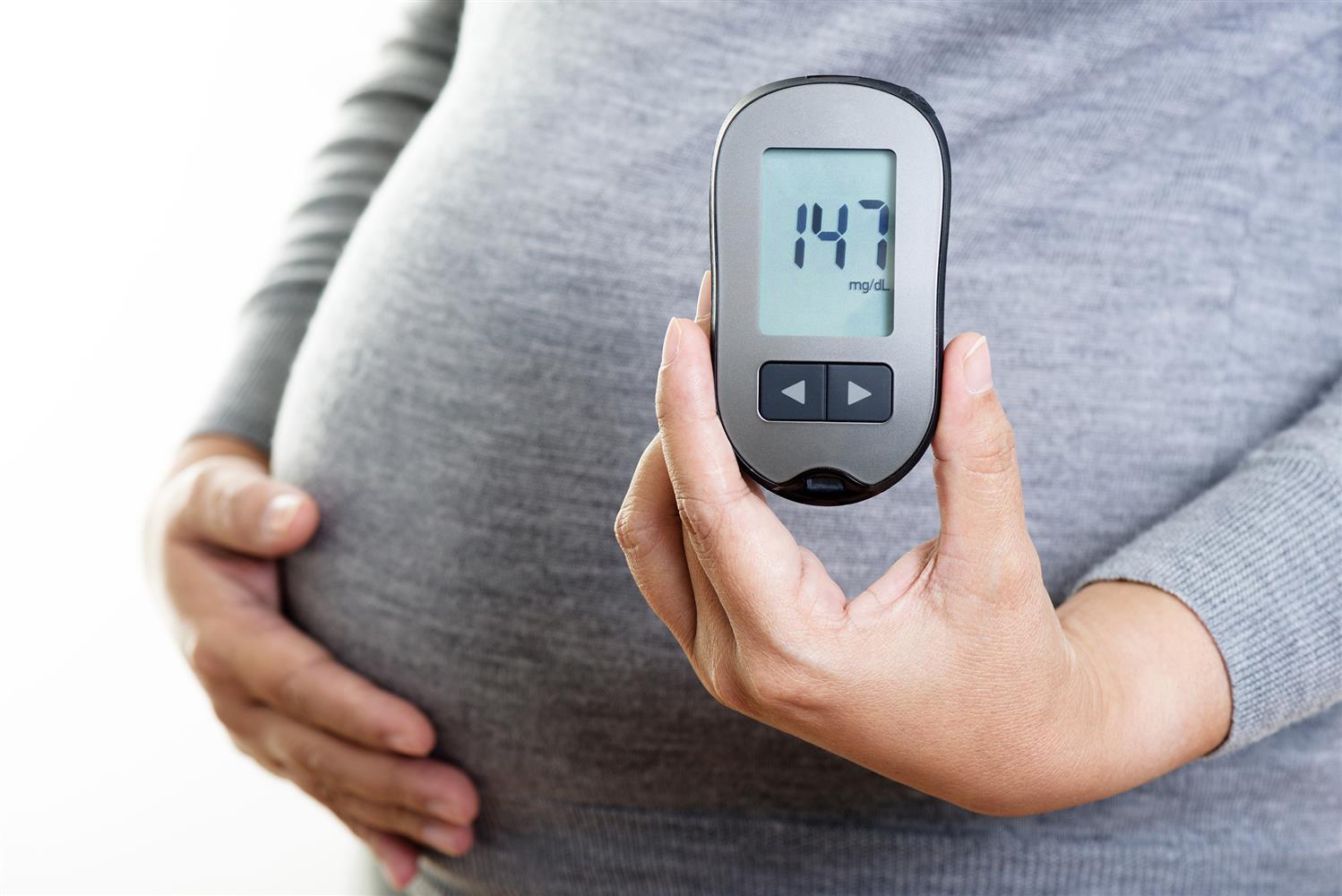
Gestational diabetes is a common pregnancy complication that affects approximately 2-10% of pregnant women. This condition occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Here are the key points to understand about gestational diabetes:
Symptoms: Often asymptomatic, but may include increased thirst and frequent urination
Diagnosis: Usually detected through routine glucose screening between 24-28 weeks of pregnancy
Risk factors: Obesity, family history of diabetes, advanced maternal age
Management of gestational diabetes typically involves:
Blood sugar monitoring
Dietary changes
Regular exercise
Insulin therapy (if necessary)
Preeclampsia
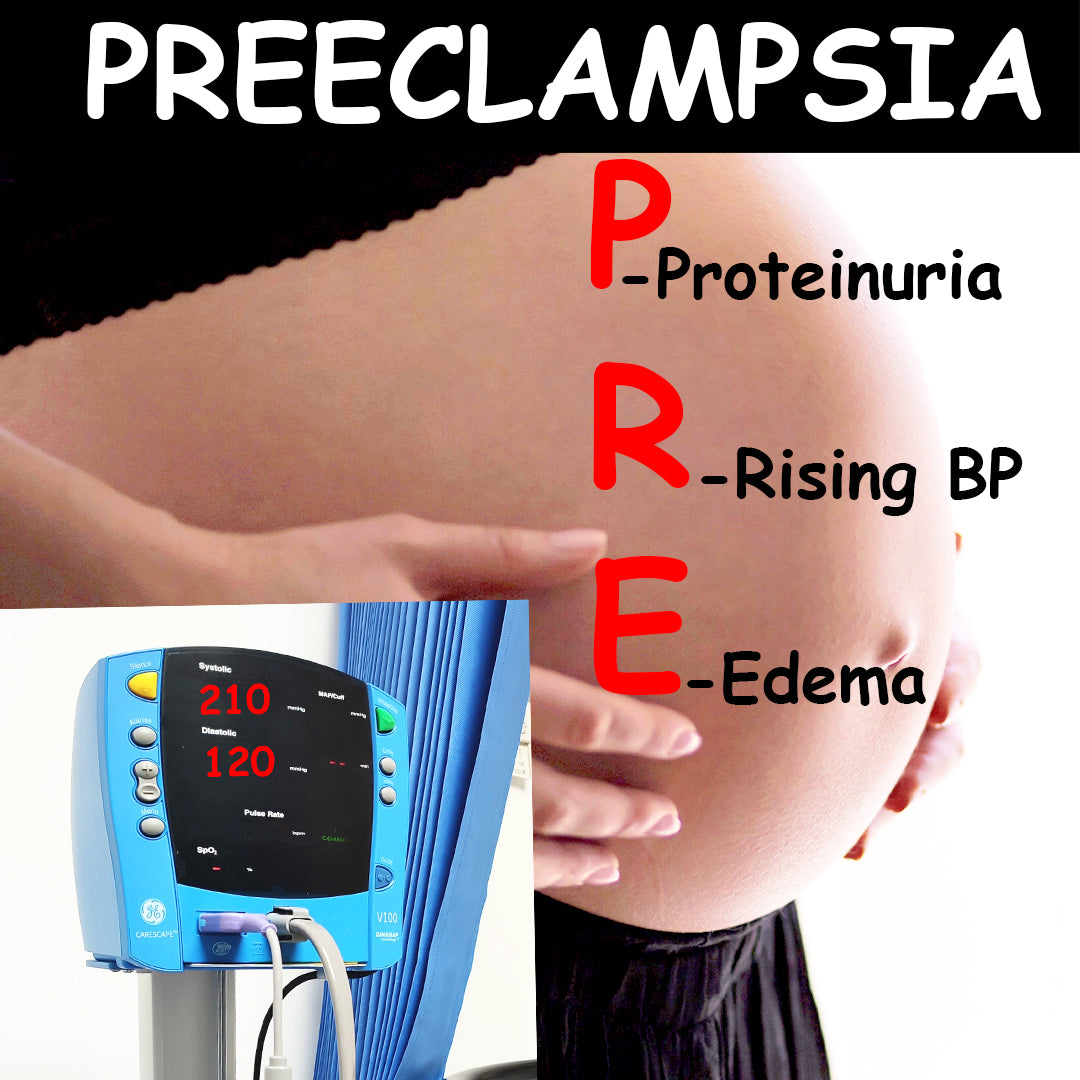
Preeclampsia is a serious pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organ systems, most often the liver and kidneys. It typically occurs after 20 weeks of pregnancy and can lead to severe complications if left untreated.
Key features of preeclampsia include:
Sudden increase in blood pressure
Protein in urine
Swelling in hands, feet, and face
Severe headaches and vision changes
Treatment options depend on the severity and gestational age but may include:
Bed rest
Blood pressure medication
Corticosteroids to improve fetal lung maturity
Early delivery if the condition becomes severe
Anemia
Anemia during pregnancy is a condition where there are not enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to the body’s tissues. It’s particularly common due to the increased blood volume and demand for iron during pregnancy.
Types of anemia in pregnancy:
| Type | Cause | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|
| Iron-deficiency anemia | Lack of iron | Fatigue, weakness, pale skin |
| Folate-deficiency anemia | Lack of folic acid | Fatigue, irritability, poor growth |
| Vitamin B12 deficiency | Lack of vitamin B12 | Fatigue, shortness of breath, numbness |
Treatment typically involves:
Iron supplements
Folic acid supplements
Vitamin B12 supplements (if necessary)
Dietary changes to include iron-rich foods
Hyperemesis gravidarum

Hyperemesis gravidarum is a severe form of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy that can lead to dehydration, weight loss, and electrolyte imbalances. It affects about 0.3-3% of pregnancies and can significantly impact a woman’s quality of life.
Symptoms of hyperemesis gravidarum include:
Severe, persistent nausea and vomiting
Dehydration
Weight loss of more than 5% of pre-pregnancy body weight
Electrolyte imbalances
Management strategies for hyperemesis gravidarum may involve:
Intravenous fluids for rehydration
Anti-nausea medications
Vitamin B6 supplements
Small, frequent meals
Ginger or acupressure bands for symptom relief
Understanding these common pregnancy complications is crucial for expectant mothers and healthcare providers alike. Early detection and proper management can significantly reduce the risks associated with these conditions and promote healthier outcomes for both mother and baby. In the next section, we’ll explore the various risk factors that can increase the likelihood of experiencing these and other pregnancy complications.
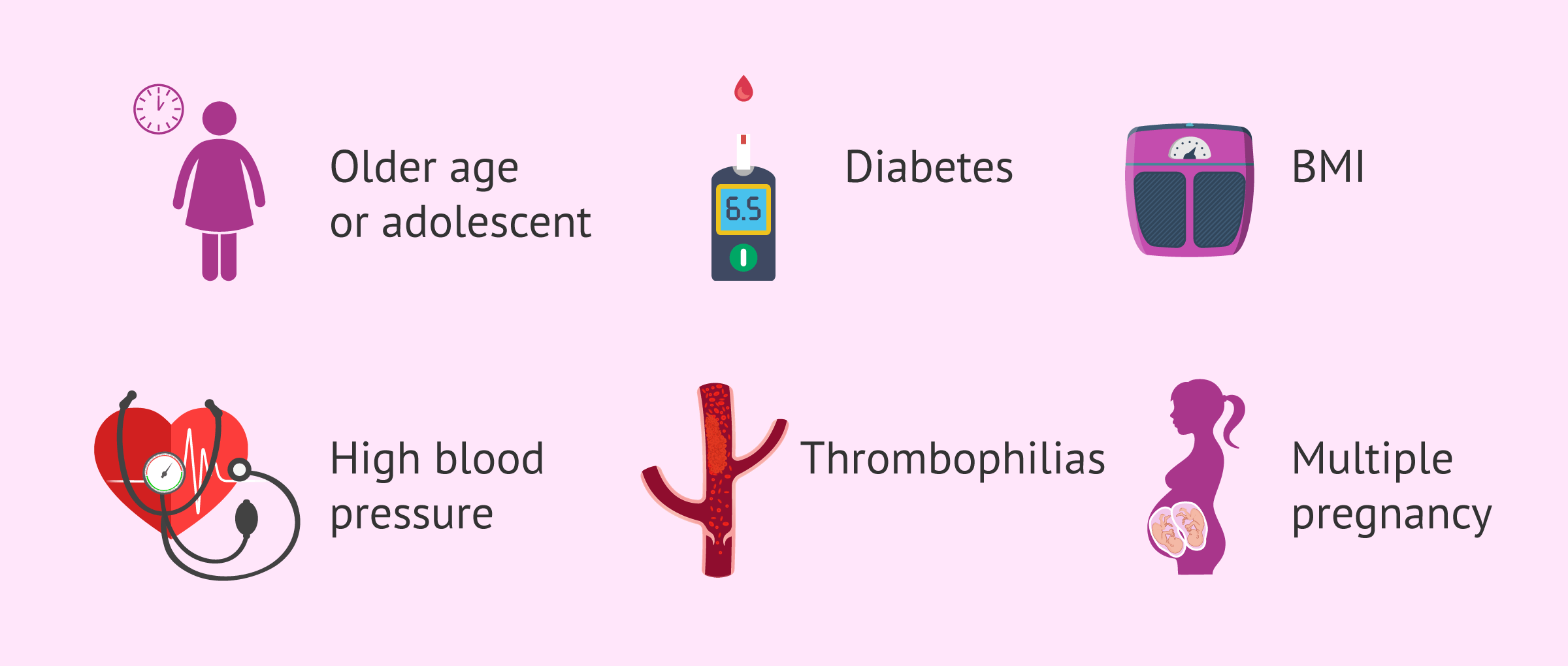
Risk Factors for Pregnancy Complications
Age plays a significant role in pregnancy outcomes. Both younger and older mothers face unique risks:
Younger mothers (under 20):
Higher risk of preeclampsia
Increased chance of preterm birth
Greater likelihood of low-birth-weight babies
Older mothers (35 and above):
Higher risk of gestational diabetes
Increased chance of chromosomal abnormalities
Greater likelihood of placenta previa
Pre-existing medical conditions
Certain health conditions can complicate pregnancy:
Diabetes
Hypertension
Thyroid disorders
Autoimmune diseases
Obesity
These conditions may increase the risk of preeclampsia, gestational diabetes, and preterm labor. Regular prenatal screening is crucial for early detection and management of potential complications.
Lifestyle factors
Daily habits and choices significantly impact pregnancy health:
| Lifestyle Factor | Potential Risks |
|---|---|
| Smoking | Low birth weight, preterm birth, birth defects |
| Alcohol consumption | Fetal alcohol spectrum disorders |
| Poor nutrition | Developmental issues, anemia |
| Lack of exercise | Gestational diabetes, excessive weight gain |
| High stress levels | Preterm labor, low birth weight |
Multiple pregnancies
Carrying twins, triplets, or more increases the likelihood of:
Preterm labor
Gestational diabetes
Preeclampsia
Low birth weight
Cesarean delivery
These pregnancies require more frequent monitoring and specialized care to manage potential complications.
Previous pregnancy complications
A history of complications in prior pregnancies can indicate a higher risk for future pregnancies. Key factors include:
Previous preterm birth
Prior cesarean section
History of preeclampsia
Previous gestational diabetes
Recurrent miscarriages
Women with these histories should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop tailored care plans for subsequent pregnancies.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for identifying high-risk pregnancies early. While some factors, like age or pre-existing conditions, cannot be changed, others can be modified through lifestyle adjustments and proper medical care. Regular prenatal check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are essential for managing these risks effectively. By being aware of these factors, expectant mothers can take proactive steps to promote a healthier pregnancy and reduce the likelihood of complications.
Preventing Pregnancy Complications
Preconception health plays a crucial role in preventing pregnancy complications. By taking proactive steps before conceiving, you can significantly reduce the risk of potential issues during pregnancy. Here are some key aspects of preconception health to consider:
Medical check-up: Schedule a comprehensive health examination with your healthcare provider.
Manage existing health conditions: Ensure any chronic conditions are well-controlled.
Update vaccinations: Get up to date on necessary immunizations.
Folic acid supplementation: Start taking folic acid supplements to prevent neural tube defects.
Maintain a healthy weight: Achieve a healthy BMI before conception.
| Preconception Health Checklist |
|---|
| ✓ Medical check-up |
| ✓ Manage existing conditions |
| ✓ Update vaccinations |
| ✓ Folic acid supplementation |
| ✓ Maintain healthy weight |
B. Regular prenatal care
Once pregnant, regular prenatal care is essential for monitoring both maternal and fetal health. These check-ups allow healthcare providers to detect and address potential complications early. Key aspects of prenatal care include:
Routine check-ups: Schedule and attend all recommended prenatal visits.
Prenatal screenings: Undergo recommended tests to detect potential issues.
Open communication: Discuss any concerns or symptoms with your healthcare provider promptly.
C. Healthy diet and exercise
Maintaining a balanced diet and engaging in appropriate exercise during pregnancy can significantly reduce the risk of complications. Consider the following guidelines:
Nutrient-rich diet:
Include a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
Avoid raw or undercooked meats, unpasteurized dairy, and high-mercury fish.
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water.
Pregnancy-safe exercise:
Engage in low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or prenatal yoga.
Aim for 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise routine.
D. Stress management
High levels of stress during pregnancy can contribute to complications such as preterm labor. Implementing effective stress management techniques is crucial:
Relaxation techniques:
Practice deep breathing exercises
Try meditation or mindfulness
Consider prenatal massage
Support system:
Connect with family and friends
Join prenatal support groups
Seek professional counseling if needed
Self-care:
Prioritize adequate sleep
Engage in hobbies or activities you enjoy
Set realistic expectations and learn to say no when necessary
By focusing on these preventive measures, expectant mothers can significantly reduce their risk of pregnancy complications. Remember that every pregnancy is unique, and it’s essential to work closely with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan tailored to your specific needs and risk factors. With proper care and attention to these preventive strategies, you can increase the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy and positive outcomes for both you and your baby.
Prioritizing prenatal care, maintaining a balanced diet, and staying physically active are essential steps in reducing the likelihood of complications. If you’re pregnant or planning to conceive, consult with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized plan for a safe and healthy pregnancy journey. Remember, early detection and proper management of any complications are key to ensuring the best possible outcomes for you and your baby.