Pineapple, a tropical wonder, offers a wealth of health benefits that may astonish regular consumers with its high concentration of vitamin C and manganese. This fruit, scientifically known as Ananas comosus, goes beyond mere refreshment; its notable nutritional profile positions it as a pillar for bolstering immunity and supporting bone health. The intake of pineapple not only tantalizes the taste buds but serves as a versatile contributor to overall well-being due to its rich ensemble of antioxidants and enzymes.
With the world becoming increasingly health-conscious, understanding pineapple benefits is crucial, especially regarding digestive health, anti-inflammatory properties, and even its potential in cancer prevention. This article delves into how the regular consumption of this succulent fruit aids in inflammation reduction, contributes to weight management, and activates metabolic processes, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet. As we explore the breadth of pineapple’s positive impact on health, it becomes clear why this fruit deserves a consistent spot on the menu.
Nutritional Profile of Pineapple
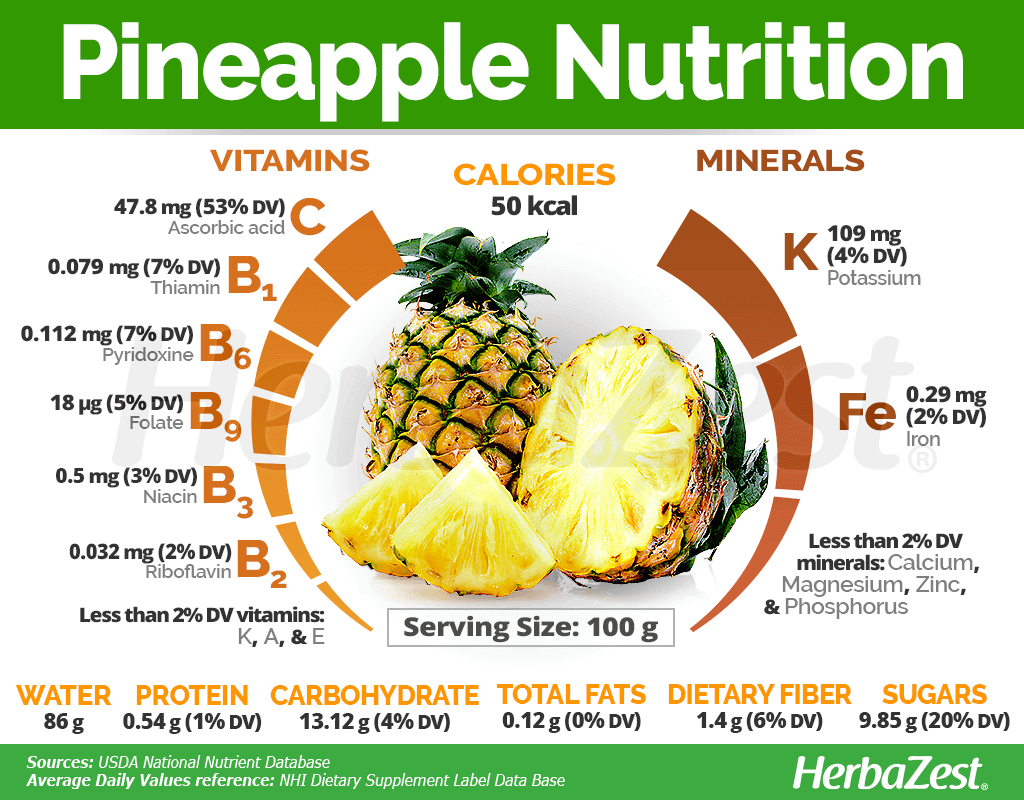
Pineapple stands out as a nutritional powerhouse with a remarkable profile that supports various aspects of health. Here’s a closer look at what one cup of this tropical fruit has to offer:
Calories, Fiber, and Protein: It contains about 83 calories, making it a low-calorie choice for a nutritious snack. Plus, with 2.3 grams of fiber, it aids in digestion and contributes to the feeling of fullness. The 1.4 grams of protein in pineapple can be a small but valuable addition to daily protein intake.
Vitamins and Minerals: This fruit is a treasure trove of essential nutrients. It provides more than 88% of the daily value of vitamin C, vital for immunity and skin health. The manganese content is impressive too, delivering over 109% of the daily value for women and 66% for men, which plays a crucial role in the metabolism of fats and carbohydrates.
Antioxidant Composition: The antioxidants in pineapple, such as flavonoids and phenolic compounds, contribute to its heart-protective effects. These compounds help combat oxidative stress and may reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Incorporating pineapple into your diet can be a delicious and smart way to enhance your nutritional intake. Its combination of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and enzymes not only supports overall health but also provides specific benefits such as aiding digestion, boosting immunity, and potentially fighting inflammation. Remember, fresh pineapple is the most nutritious form, so enjoy it in its natural state whenever possible to reap the full range of pineapple benefits.
Read: Unlock the Secrets of Guava Fruit & Leaves: 8 Health Benefits You Need to Know
Digestive Health Benefits
/assets/images/provider/photos/2808133.png)
Pineapple’s impressive digestive health benefits are largely attributed to the presence of bromelain, a group of enzymes that play a crucial role in breaking down proteins and aiding digestion. Here’s how pineapple can support digestive health:
Enzymatic Power: Bromelain in pineapple assists in protein digestion, which is particularly beneficial after consuming meals high in protein. This can help prevent feelings of heaviness and discomfort often associated with protein-rich diets.
Fiber for Fullness: With a substantial fiber content, pineapple promotes a sense of satiety. This not only helps control appetite but also supports regular bowel movements, contributing to overall digestive well-being.
Anti-Inflammatory Action: Bromelain’s anti-inflammatory properties can soothe the gut and colon. This may alleviate symptoms like bloating, gas, and cramping, making pineapple a soothing choice for those with sensitive digestive systems.
Additionally, pineapple’s enzymes have been known to offer relief from constipation, gas, and bloating by breaking down proteins in the gut. For individuals with pancreatic insufficiency, the digestive support from bromelain can be particularly helpful. It’s worth noting that while bromelain may boost metabolism, it doesn’t directly cause weight loss; however, the fiber in pineapple can help manage weight by reducing overeating. Whether you’re looking to enhance your post-workout recovery with muscle soreness reduction or seeking a natural way to support your digestive health, incorporating pineapple into your diet could be a delightful and healthful choice.
Immune System Support

Pineapple’s role in supporting the immune system is significant, thanks to its rich content of vitamin C and the enzyme bromelain. These components work together to fortify the body’s defenses against illness. Here’s how pineapple contributes to a stronger immune system:
Antioxidant Action: Pineapple is abundant in vitamin C, a potent antioxidant that helps prevent oxidative damage to cells, which can lead to chronic diseases. The fruit’s antioxidants also include bromelain, which contributes to its immune-supporting capabilities.
Viral and Bacterial Infection Reduction: A study involving children showed that regular consumption of canned pineapple reduced the incidence of viral and bacterial infections. This suggests that including pineapple in one’s diet could be beneficial for enhancing immunity.
Bromelain’s Benefits: This enzyme not only aids digestion but also boasts antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties. It is stable in the gut, maintaining its concentration and activity for several hours post-ingestion. Bromelain’s mucolytic properties are advantageous for managing respiratory inflammation related to allergies, influenza, and asthma.
Moreover, bromelain’s antibacterial and potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 virus inhibitory effects could be instrumental in managing viral infections, including those secondary to COVID-19. By incorporating pineapple into your diet, you harness these pineapple benefits to support your immune system, potentially lowering cancer risk and improving recovery post-surgery, all while enjoying the sweet taste of this tropical fruit.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties

Pineapple’s nutritional profile, particularly its bromelain content, offers a range of anti-inflammatory benefits, which can play a crucial role in overall health and healing. Here are several ways in which these properties manifest:
- Heart Health: Bromelain may reduce the risk of heart disease by breaking down blood clots and cholesterol deposits, ensuring healthy blood flow. Its lipid-lowering capabilities, supported by pineapple’s antioxidants, further benefit heart health.
- Respiratory Relief: By thinning mucus, bromelain can alleviate congestion and relieve symptoms associated with the common cold, allergies, and asthma. Studies indicate a reduction in airway inflammation, a primary symptom of asthma, through regular bromelain intake.
- Joint and Tissue Support: Individuals with arthritis may find relief from joint pain due to the anti-inflammatory effects of bromelain. It also promotes tissue healing and may reduce recovery time post-exercise or surgery.
Incorporating pineapple into your diet can thus be a strategic choice for those seeking natural anti-inflammatory options. Whether it’s enhancing fertility, speeding up healing, or managing conditions like arthritis and asthma, the benefits of pineapple’s bromelain enzyme are significant and diverse. Its ability to ease joint pain, combat inflammation, and potentially suppress tumor growth showcases the power of this tropical fruit as more than just a tasty snack. Regular consumption can be a simple yet effective way to tap into these health perks.
Cancer-Fighting Potential

Pineapple’s potential in cancer prevention and treatment is gaining recognition due to the presence of bromelain, an enzyme with notable anti-cancer properties. Here’s how this tropical fruit could contribute to fighting cancer:
Bromelain’s Anti-Cancer Effects:
- Inhibits growth of breast cancer cells.
- Upregulates pro-apoptotic factors that encourage the death of cancer cells.
- Downregulates anti-apoptotic factors, preventing cancer cells from evading death.
- Promotes apoptosis, the programmed cell death, through specific signaling pathways such as c-Jun N-terminal kinase and p38 kinase.
Enhancing Chemo-Efficiency:
- Bromelain-loaded nanoparticles and nanoemulsions have been shown to improve chemotherapy outcomes by enhancing chemosensitivity, improving apoptosis, and reducing tumor weight in breast cancer cells.
- When combined with chemotherapeutic drugs like cisplatin, bromelain exhibits synergistic effects, inducing apoptosis in breast cancer cells through mitochondria-mediated pathways.
Pineapple Juice and Cancer Cell Growth:
- Laboratory studies reveal that pineapple juice can inhibit the growth of breast and colon cancer cells in vitro.
- Pineapple vinegar has shown to reduce tumor mass and volume in breast cancer-challenged mice, suggesting its potential as a chemopreventative agent.
- The consumption of pineapple and its bioactive compounds can be particularly effective in breast cancer due to their synergistic interactions with chemotherapeutic drugs, enhancing drug efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Pineapple’s rich antioxidant content, including flavonoids and phenolic compounds, further supports its role in cancer prevention by potentially reducing the risk of various cancers. Regular, moderate consumption of pineapple can promote overall health and may play a role in preventing serious health conditions, making it a valuable addition to a balanced diet.
Pineapple in Weight Management and Metabolism
Pineapple, a low-calorie fruit with high water and fiber content, offers benefits for those looking to manage their weight. The fiber in pineapple contributes to feelings of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating. However, its natural sugar content means it should be enjoyed in moderation to avoid excessive calorie intake, which could impede weight loss efforts. Here are the key considerations for including pineapple in a weight management plan:
Hydration and Satiety: The high water content in pineapple helps maintain hydration and may help prevent overeating by promoting a sense of fullness.
Balance and Moderation: While pineapple is beneficial for weight loss, it’s important to consume it in moderation due to its sugar content. Overindulgence can lead to heartburn or discomfort and can counteract weight loss goals.
Comprehensive Approach: For effective weight management, pineapple should be part of a balanced diet coupled with regular exercise.
Some individuals may need to avoid pineapple due to allergies or specific health conditions like contact dermatitis. Additionally, pineapple’s antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties can support heart health and may aid in fat burning, although more evidence is needed to confirm this effect. Pineapple is also a valuable source of copper and manganese, which are important for bone health. In particular, post-menopausal women may benefit from manganese-rich foods like pineapple to prevent bone loss.
Conclusion
Through our exploration of the healthful bounty of pineapple, it has become evident that this tropical fruit stands as more than a mere delight to the palate; it is a robust ally to our well-being. Rich in essential nutrients, enzymes, and antioxidants, pineapple extends its benefits across various aspects of health, from improving digestion and bolstering the immune system to showcasing potential anti-cancer properties. The broad spectrum of advantages attributed to regular pineapple consumption underscores the fruit’s role in promoting overall health and serving as a tasty component of a balanced diet.
The practice of integrating pineapple into meals not only catalyzes a positive impact on physical health but also aligns harmoniously with a health-conscious lifestyle. As we consider the full scope of pineapple’s perks, it is encouraging to recognize how such simple dietary choices can have profound implications for our well-being. For those inspired to make pineapple a staple in their journey to better health, remember moderation is key, and always relish the journey to wellness.


