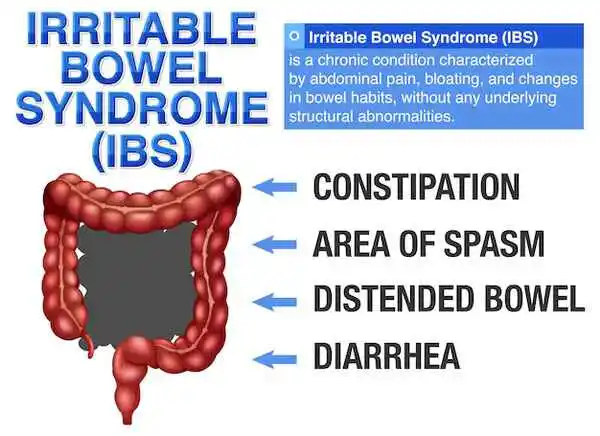
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that affects the large intestine. It is a common condition that causes a variety of symptoms, including abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea, and constipation. IBS is a functional disorder, which means that there are no structural abnormalities in the digestive system, but the bowel functions are impaired.
The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but there are several factors that may contribute to its development. These include abnormalities in the gut-brain axis, increased sensitivity of the intestines, and changes in the gut microbiota. Stress and certain foods can also trigger symptoms in individuals with IBS.
Common causes of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
While the exact cause of IBS is not fully understood, there are several common factors that may contribute to its development. These include:
- Gut-brain axis abnormalities: The gut and the brain are connected through a complex network of nerves, hormones, and chemicals. Disruptions in this communication can lead to changes in bowel function, contributing to the development of IBS.
- Intestinal sensitivity: Individuals with IBS often have increased sensitivity in their intestines, which can lead to pain and discomfort.
- Changes in gut microbiota: The gut is home to trillions of bacteria that play a crucial role in digestion and overall health. Imbalances in the gut microbiota have been linked to the development of IBS.
- Food triggers: Certain foods and drinks, such as caffeine, alcohol, and spicy foods, can trigger symptoms in individuals with IBS. Keeping a food diary can help identify these triggers and manage symptoms.
Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
The symptoms of IBS can vary from person to person, but the most common ones include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping: This is one of the hallmark symptoms of IBS. The pain is often relieved by bowel movements.
- Bloating and gas: Many individuals with IBS experience excessive gas and bloating, which can be uncomfortable and embarrassing.
- Diarrhea and/or constipation: IBS can cause changes in bowel habits, leading to either frequent loose stools or infrequent, hard stools.
- Mucus in the stool: Some individuals with IBS may notice the presence of mucus in their stools.
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances: The chronic nature of IBS can lead to fatigue and disrupted sleep patterns.
It’s important to note that these symptoms can overlap with other digestive disorders, so it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Diagnosing IBS can be challenging because there are no specific tests or markers for the condition. Instead, healthcare professionals rely on a combination of medical history, physical examination, and the Rome criteria, which are a set of guidelines used to diagnose functional gastrointestinal disorders.
During the diagnostic process, your healthcare provider will ask detailed questions about your symptoms, perform a physical examination, and may order additional tests to rule out other conditions. These tests may include blood tests, stool tests, and imaging studies.
The role of diet in managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Diet plays a crucial role in managing IBS symptoms. Certain foods and drinks can trigger symptoms, while others can help alleviate them. It’s important to identify and avoid trigger foods while ensuring a well-balanced diet.
- Keeping a food diary: Keeping a record of your meals and symptoms can help identify trigger foods. Common trigger foods include spicy foods, fatty foods, caffeine, and alcohol.
- Low FODMAP diet: FODMAPs are a group of carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the intestines and can trigger IBS symptoms. Following a low FODMAP diet, under the guidance of a registered dietitian, can help manage symptoms for many individuals with IBS.
- Probiotics: Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help restore the balance of gut microbiota. They have been shown to alleviate symptoms in some individuals with IBS. However, it’s important to choose the right strain and consult with a healthcare professional before starting a probiotic regimen.
Read: Importance of Fiber: The Key to a Healthy Diet | Foods Rich in Fiber!
High fiber diet for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Fiber is an essential component of a healthy diet, and it can play a significant role in managing IBS symptoms. However, it’s important to note that not all types of fiber are created equal when it comes to IBS.
- Soluble fiber: Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance in the intestines. It can help regulate bowel movements and alleviate diarrhea.
- Insoluble fiber: Insoluble fiber adds bulk to the stool and can help alleviate constipation.
It’s important to increase fiber intake gradually to avoid exacerbating symptoms. Good sources of soluble fiber include oats, bananas, and legumes, while insoluble fiber can be found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Other treatment options for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
In addition to dietary changes, there are several other treatment options available for individuals with IBS. These include:
- Medications: Depending on the predominant symptoms, your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to help manage pain, regulate bowel movements, or reduce inflammation.
- Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): CBT is a type of therapy that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors. It has been shown to be effective in managing IBS symptoms by reducing stress and improving coping mechanisms.
- Stress management techniques: Stress can exacerbate IBS symptoms, so it’s important to find healthy ways to manage stress. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and exercise can help reduce stress levels.
How long does Irritable Bowel Syndrome last?
The duration of IBS can vary from person to person. For some individuals, symptoms may come and go, while for others, they may be persistent. IBS is a chronic condition, which means that it is long-term and requires ongoing management. However, with the right treatment plan and lifestyle modifications, it is possible to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lifestyle changes to manage Irritable Bowel Syndrome
In addition to dietary changes and medical treatments, certain lifestyle modifications can help manage IBS symptoms. These include:
- Regular exercise: Exercise has been shown to have a positive impact on gut health and can help regulate bowel movements.
- Stress reduction: Stress can trigger or exacerbate IBS symptoms, so finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as through exercise, meditation, or hobbies, is crucial.
- Sleep hygiene: Establishing a regular sleep routine and practicing good sleep hygiene can help improve sleep quality and reduce fatigue associated with IBS.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking plenty of water throughout the day can help regulate bowel movements and prevent dehydration.
Conclusion
Irritable Bowel Syndrome is a common gastrointestinal disorder that can significantly impact quality of life. While the exact cause is unknown, there are several factors that may contribute to its development. By understanding the common causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals with IBS can work with healthcare professionals to effectively manage their symptoms. Lifestyle modifications, dietary changes, and medical treatments can all play a role in improving symptoms and overall well-being. If you suspect you may have IBS, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.